What is Computed Tomography (CT)?
Computed Tomography, commonly known as CT scanning, is a diagnostic imaging method that allows the detection of various diseases and pathological conditions. During a CT scan, the information obtained is processed by the system to create a complete, detailed image of the organs and body systems. This makes it possible to distinguish anatomical and physiological changes in the organs.
CT is a painless, non-invasive diagnostic method based on X-ray technology.
Which organs can be examined with CT?
CT can be used to examine:
-
Organs of the chest
-
Organs and systems of the abdominal and retroperitoneal cavities
-
Pelvic organs
-
Cardiovascular system
-
Ear–nose–throat (ENT) structures
-
Musculoskeletal system
CT is particularly effective for detecting benign and malignant tumors, even when they are small, and for determining their nature and extent.
How to prepare for a CT scan
No special preparation is required for most CT examinations.
Fasting is usually not necessary, and regular medications do not need to be withheld.
In general, no preparation is needed before CT scans of the head, neck, or chest.
What is CT Angiography?
For the evaluation of abdominal and pelvic organs, a CT angiography (CT with contrast) may be prescribed.
In such cases, some preparation is necessary.
If a contrast-enhanced CT scan is planned, the patient must first undergo a blood biochemical test to determine creatinine levels. Elevated creatinine is a contraindication for CT angiography.
If creatinine levels are within normal range, contrast material is injected prior to the scan, allowing for clearer and more detailed images.
The last meal should be taken 2–3 hours before the scan.
The contrast agent is typically eliminated from the body within 24 hours.
Contraindications for CT
There are no absolute contraindications for CT.
Relative contraindications usually relate to the use of contrast dye and include:
-
Allergic diseases, especially bronchial asthma
-
Allergy to iodine-containing solutions
-
Hyperthyroidism
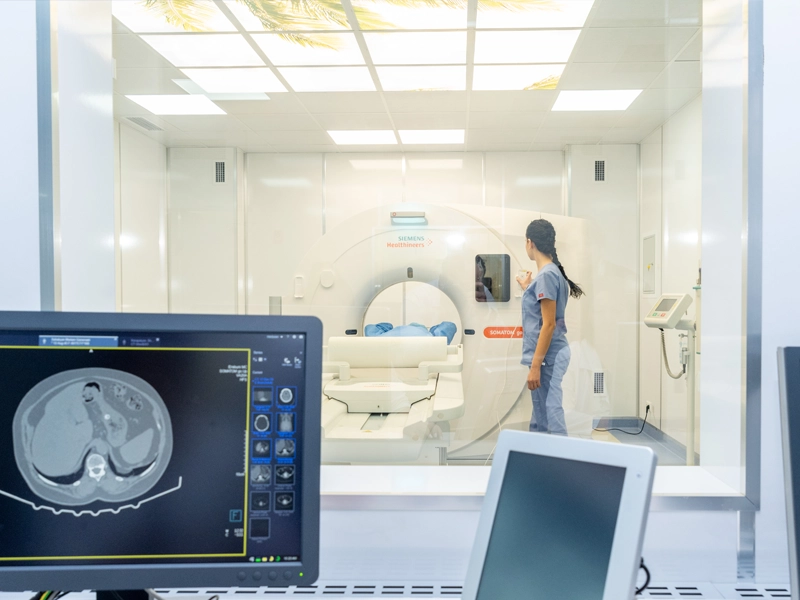
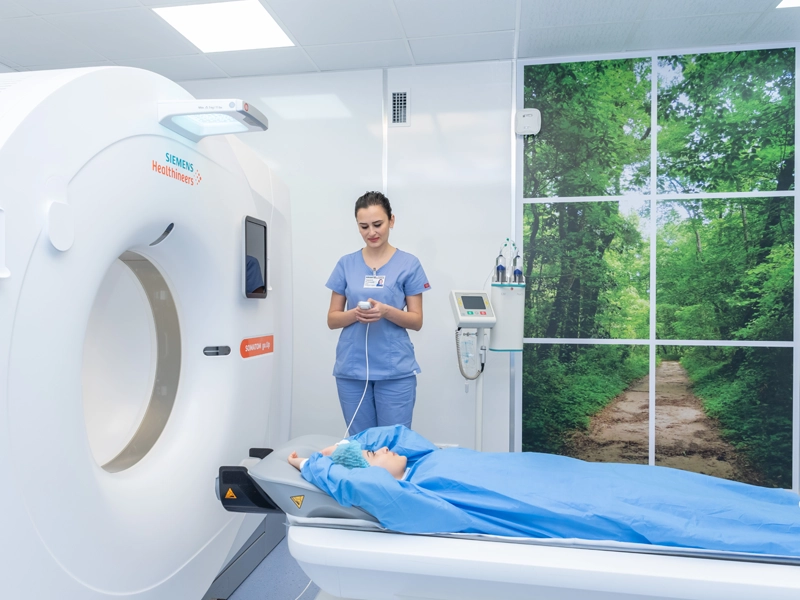
What happens during a CT scan?
Throughout the procedure, the patient lies on the examination table.
Depending on the organ being examined, the scan typically lasts 10–30 minutes.
CT and pregnancy
CT may be performed on pregnant women only when absolutely necessary.
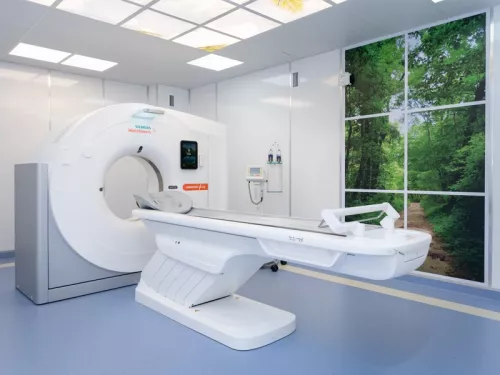
Advantages of the CT service at Erebouni Medical Center
The CT service at Erebouni Medical Center is equipped with SIEMENS Healthineers SOMATOM GO UP scanners.
Thanks to advanced engineering solutions:
-
Examination time is reduced by 1.5 times
-
Radiation dose is reduced by 4–6 times
-
The amount of contrast agent required is minimized
-
Image quality is fully preserved
The CT department is located on the 1st floor, to the right of the main entrance.
Price list
Computed tomography (CT) of one anatomical region
40,000
Computed tomography (CT) of one anatomical region with angiography
70,000
Computed tomography (CT) of two anatomical regions
50,000
Computed tomography (CT) of two anatomical regions with angiography
80,000
Computed tomography (CT) of three or more anatomical regions
60,000
Computed tomography (CT) of three anatomical regions with angiography
90,000
CT scan of the paranasal sinuses
20,000
Computed tomography (CT) of the orbits, eyeballs, and retrobulbar space
20,000
Computed tomography (CT) of the joints, simple cases
30,000
Cost of contrast agent used during computed tomography angiography
30,000
Computed tomography (CT) of one anatomical region without intravenous contrast administration; co-payment for social beneficiaries
10,000
Computed tomography (CT) of two anatomical regions without intravenous contrast administration; co-payment for social beneficiaries
15,000
Computed tomography (CT) of three or more anatomical regions without intravenous contrast administration; co-payment for social beneficiaries
20,000
Computed tomography (CT) angiography of one anatomical region or computed tomography with intravenous contrast administration, including the cost of the contrast agent; co-payment for social beneficiaries
17,500
Computed tomography (CT) angiography of two anatomical regions or computed tomography with intravenous contrast administration, including the cost of the contrast agent; co-payment for social beneficiaries
22,500
Computed tomography (CT) angiography of three anatomical regions or computed tomography with intravenous contrast administration, including the cost of the contrast agent; co-payment for social beneficiaries
27,500
Urography — computed tomography (CT) of one part, including the cost of contrast material
50,000
Computed tomography (CT) of four or more anatomical regions with angiography
110,000
CT scan of the temporal bones
20,000
Tips before a medical examination
How to Preparate for a CT Scan
There are no specific restrictions for a computed tomography (CT) examination. In most cases, no special preparation is needed prior to scans of the head, neck, and chest.
Fasting is not required, and you may continue taking any prescribed daily medications.
To undergo the examination under Universal Health Insurance or other programs, prior reimbursement approval must be obtained from the relevant services. Otherwise, the examination can only be carried out on a paid basis.
How to Prepare for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Angiography
What are the contraindications for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)?
Joint prostheses or other orthopedic devices may be considered contraindications for MRI. However, they are usually made of materials compatible with MRI, so in most cases, they do not prevent the examination.
If you have joint prostheses or other orthopedic devices, you must provide the following documentation to the MRI Service before the examination:
- A discharge summary (epicrisis)
- MRI results of the same or adjacent area post-implantation
- Implantation certificate
- Equipment passport, including the manufacturer's brand and model series
- Documentation proving MRI compatibility if the prosthesis is more than 20 years old
Stents, cava filters, and vascular shunts implanted in the body are not considered contraindications for MRI examinations.
In most cases, pacemakers are contraindicated for MRI. However, some models allow temporary deactivation during the procedure, but this must be addressed with an arrhythmologist beforehand.
Unlike portable hearing aids, cochlear implants are often incompatible with MRI, as the equipment may get damaged, particularly for scans above the knee.
Postoperative clips, sutures, and metal wires following sternotomy are generally compatible with MRI and are not considered contraindications.
From the second trimester of pregnancy, MRI can be performed without restrictions.
For gynecological conditions, the examination is typically scheduled for any day after the menstrual cycle ends.
Preparation Guidelines:
- Do not eat for 3-4 hours before the examination.
- Bring any previous diagnostic results (discs, images, lab test results) along with relevant medical documents, such as discharge summaries (epicrisis).
- A bowel cleanse may be required before the MRI, and the medication regimen should be discussed with your physician.
- Avoid eating for 6 hours and drinking fluids for 2 hours before the procedure.
To undergo the examination under Universal Health Insurance or other programs, prior reimbursement approval must be obtained from the relevant services. Otherwise, the examination can only be carried out on a paid basis.
Siemens Healthineers: Somatom go.Up



.webp)

